When investing in real estate, access to accurate sales data is crucial for making informed decisions. However, not all states in the U.S. provide the same level of transparency regarding real estate transactions. Some states openly disclose property sale prices, while others keep this information private. These states are categorized as disclosure and non-disclosure states.
Understanding the difference between these classifications can help real estate investors, professionals, and homebuyers navigate property valuation, deal sourcing, and market analysis. This blog will break down the key differences, list which states fall into each category, and explain the impact on real estate professionals.
What Are Disclosure States?
Disclosure states allow public access to real estate sale prices. In these states, transaction details are recorded in county offices or online databases, making them easily accessible to appraisers, investors, and real estate professionals. This transparency aids in easy property valuation, market research, and accurate investment decision making.
Benefits of Disclosure States:
- Easier Property Comparisons – With publicly available sales data, investors and agents can analyze comparable sales (comps) more accurately.
- More Reliable Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) – Public data helps in refining property valuations used by lenders and platforms.
- Better Market Transparency – Buyers and sellers have a clearer understanding of market trends and property values.
Examples of Disclosure States:
Some of the major disclosure states include:
In these states, real estate professionals and the general public can access sales data through county records, online databases, or real estate platforms like Batchleads shown in the example below.

View off market & on market properties across Phoenix,AZ
What Are Non-Disclosure States?
Non-disclosure states do not publicly disclose real estate sales prices. This means that the final sale price of a property is not part of public records, making it challenging for investors and buyers to determine accurate property values.
Challenges in Non-Disclosure States:
- Limited Access to Sales Data – Investors and homebuyers must rely on alternative sources, such as MLS Listings Data or proprietary databases.
- Increased Dependence on Real Estate Professionals – Appraisers, real estate agents, and specialized data platforms become essential for obtaining property sales insights.
- More Guesswork in Property Valuation – Without access to official sales records, market analysis relies more on indirect estimates.
Examples of Non-Disclosure States:
The following states are classified as non-disclosure states:
- Alaska
- Idaho
- Kansas
- Louisiana
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- New Mexico
- North Dakota
- Texas
- Utah
- Wyoming
In these states, property sale prices are typically only available through MLS Listing platforms, appraisers, or proprietary real estate data providers like Batchleads.

How Non-Disclosure States Impact Real Estate Investors
Investors operating in non-disclosure states face unique challenges when sourcing property data. Without public sales data, they must find alternative ways to evaluate deals and estimate property values.
1. Importance of MLS Listings and Private Databases
Since non-disclosure states do not provide public sales records, real estate professionals must rely on MLS listings and proprietary databases like BatchLeads to access sales history. These platforms compile information from various sources to help investors make informed decisions.
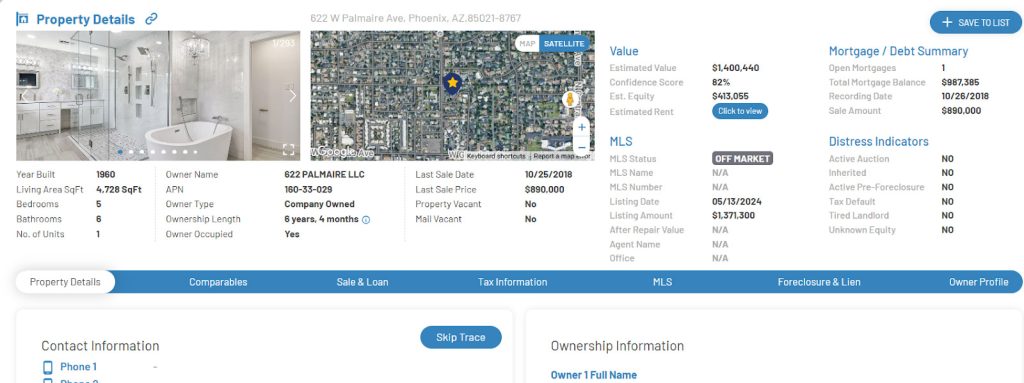
Property details preview on Batchleads
2. Challenges for Automated Valuation Models (AVMs)
AVMs rely on past sales data to generate property valuations. In non-disclosure states, limited data availability can result in less accurate estimates, making it crucial to cross-check multiple sources before making an investment decision.
3. Need for Stronger Networking with Local Professionals
Working closely with local real estate agents, appraisers, and title companies is essential in non-disclosure states. These professionals often have access to transaction data that is not publicly available, helping investors make more accurate valuations.
Strategies for Navigating Non-Disclosure States
Despite the challenges, investors can still operate successfully in non-disclosure states by using strategic approaches:
1. Leverage a Real Estate Data Platform
Getting access to top tier and accurate real estate data is a no brainer when you are in the real estate space. BatchLeads provide valuable insights into property sales, AI based propensity to sell rankings that help investors access quality property data that is otherwise unavailable.
If you like to read more on AI in Real Estate : A Game Changer check out this blog
2. Work with Local Real Estate Professionals
Building relationships with real estate agents, appraisers, and title companies can provide access to key insights and unpublished sales data.
3. Use Alternative Data Sources
In the absence of public records, investors can analyze property tax assessments, mortgage recordings, and listing prices to estimate market values.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between disclosure and non-disclosure states is crucial for anyone involved in real estate investing or property valuation. While disclosure states offer greater transparency and easier access to sales data, non-disclosure states require more effort to obtain reliable information.
By leveraging MLS Listings data, working with local professionals, and using specialized platforms like BatchLeads, real estate investors can overcome these challenges and make data-driven decisions, regardless of the state they’re operating in.